If you need to build an ApplicationContext hierarchy (multiple contexts with a parent/child relationship) or if you prefer using a “fluent” builder API, you can use the SpringApplicationBuilder.
假若需要建立ApplicationContext(容器) 繼承關係,或是使用者偏好流順的建立API ,那麼可以使用
SpringApplicationBuilder。
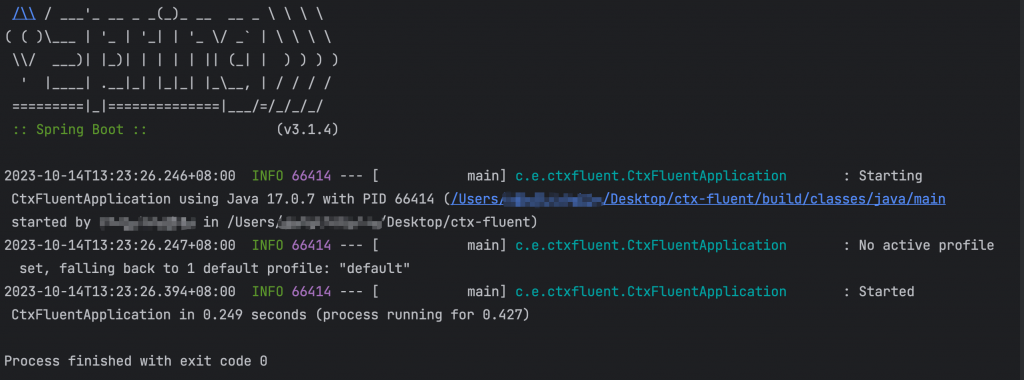
直接採用 class SpringApplication 啟動 application,得到下方畫面
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CtxFluentApplication.class, args);
}
這裡採用 Fluent Builder API 啟動 application (這裡只填入 父類別的註冊類別)
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SpringApplicationBuilder().parent(ParentConfig.class)
.web(WebApplicationType.NONE)
.run(args);
}
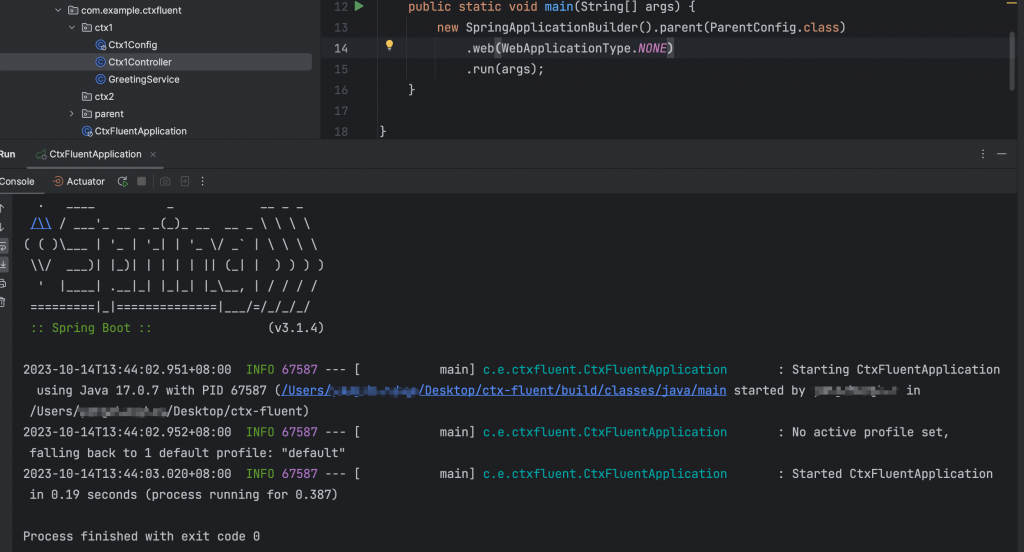
此時,啟動application啟動完就會關閉,因為WebApplicationType.NONE 就是當作一般 Java 程式。
Parent 註冊類別
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
public class ParentConfig {
}
@ComponentScan 採用預設值會自動掃描 class ParentConfig 所在 /parent 的內容
Parent Service Interface
public interface IHomeService {
String getGreeting();
}
Parent Service
@Service
public class HomeService implements IHomeService{
@Override
public String getGreeting() {
return "Welcome User";
}
}
child one 自己實作介面
@Service
public class GreetingService implements IHomeService {
@Override
public String getGreeting() {
return "Greetings for the day";
}
}
child one’s configuration
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
@PropertySource("classpath:ctx1.properties")
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class Ctx1Config {
@Bean
public IHomeService homeService() {
return new GreetingService();
}
}
透過 @PropertySource 去讀取不同的 Properties
child one’s controller
@RestController
public class Ctx1Controller {
@Autowired
private IHomeService homeService;
@GetMapping("/home")
public String greeting() {
return homeService.getGreeting();
}
}
child two’s configuration
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@PropertySource("classpath:ctx2.properties")
public class Ctx2Config {
}
child two’s controller
@RestController
public class Ctx2Controller {
@Autowired
private IHomeService homeService;
@GetMapping("/greeting")
public String getGreeting() {
return homeService.getGreeting();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SpringApplicationBuilder().parent(
ParentConfig.class)
.web(WebApplicationType.NONE)
.child(Ctx1Config.class)
.web(WebApplicationType.SERVLET)
.sibling(Ctx2Config.class)
.web(WebApplicationType.SERVLET)
.run(args);
}
這裡透過 SpringApplicationBuilder 去建立 parent 的 context,在透過 child 去建立第一個 child context 之後透過 sibling 去建立第二個 child context ,這裡有一個疑問,如果第二個child ctx2 也是用 child 去建立會發生什麼事情?
程式碼,只會完成一個context 的建立。 至於為什麼?
SpringApplicationBuilder.child 會另外開一個 Builder 並將之回傳
public SpringApplicationBuilder child(Class<?>... sources) {
SpringApplicationBuilder child = new SpringApplicationBuilder();
child.sources(sources);
//省略以下內容
return child;
}
所以後面builder chain 的時候,就是以child 去的角度去建立context,自然是 chlid’s sibling,
而不是 child’s child 。
ctx1.properties(Child one)
server.port=8074
server.servlet.context-path=/ctx1
spring.application.admin.enabled=false
spring.application.admin.jmx-name=org.springframework.boot:type=Ctx1Rest,name=Ctx1Application
ctx1.properties(Child two)
server.port=8075
server.servlet.context-path=/ctx2
spring.application.admin.enabled=false
spring.application.admin.jmx-name=org.springframework.boot:type=WebAdmin,name=SpringWebApplication
這裡application 會啟監聽不同port號的tomcat server,註冊檔有刻意切割兩個Root URI。
下方為啟動應用時的log,第一段是啟動 Parent 的部分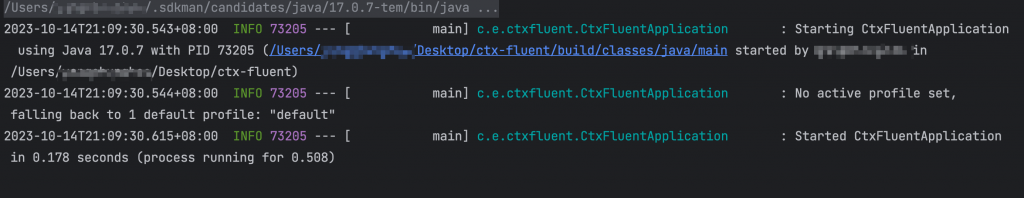
log 第二段是第一個 child ctx1 的 tomcat 啟動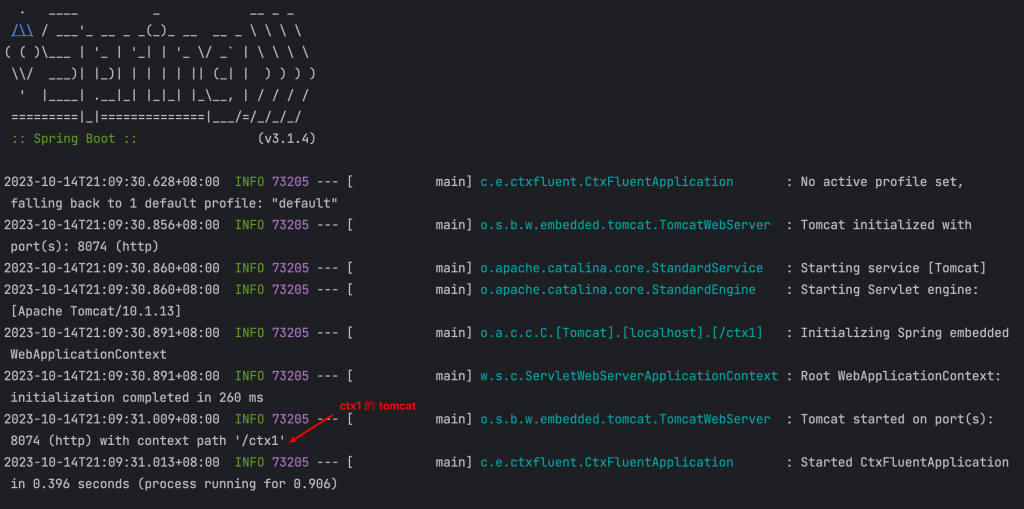
log第三段是第二個child ctx2 的 tomcat 啟動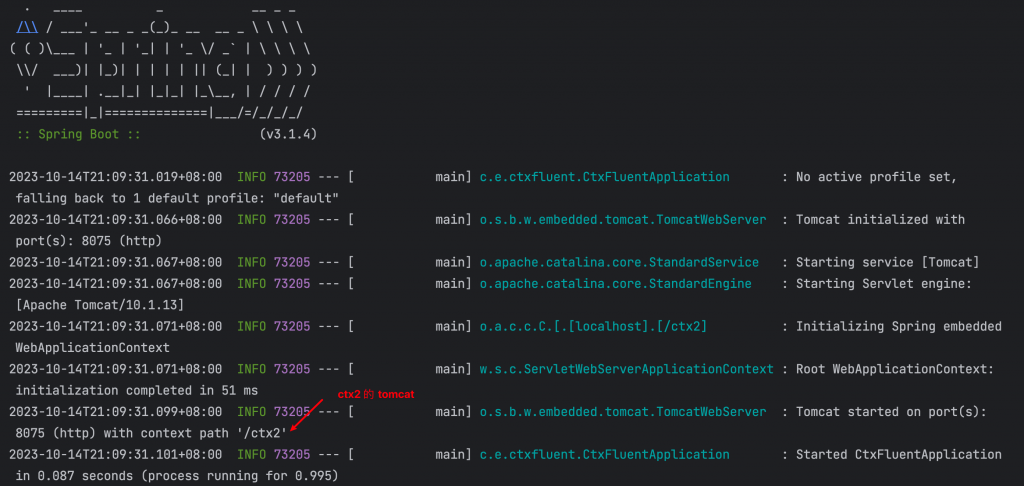
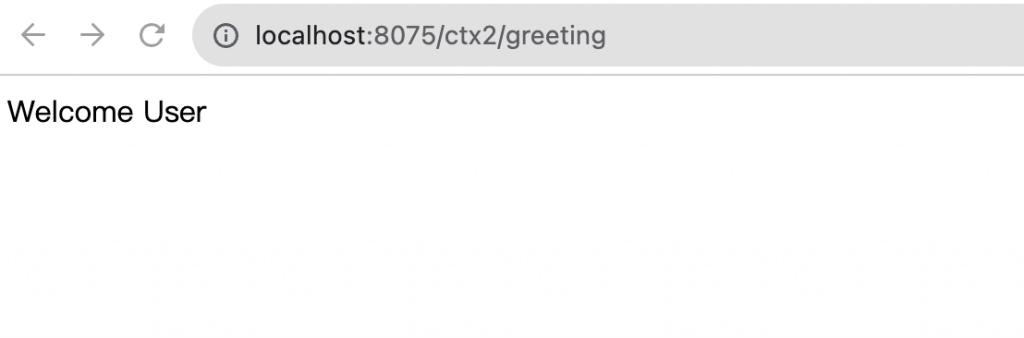
下方為 API 回應的 log,透過不同URL 打兩個child 的 API 發現,ctx1 有自己實作 IHomeService,所以這時候注入的會是child 自己實作的 service(由打印內容可以知道是ctx1 是用自己實作的service),而 ctx2 是用 parent 實作的 service。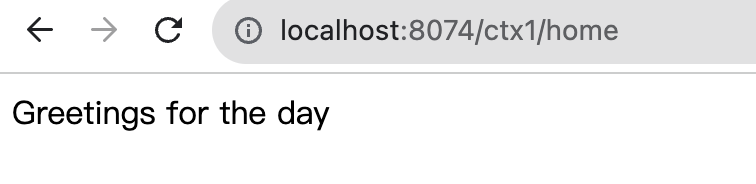
參考資料
{官方} SpringApplicationBuilder
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/api/org/springframework/boot/builder/SpringApplicationBuilder.html
Context Hierarchy with the Spring Boot Fluent Builder API
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-boot-context-hierarchy
